In the world of industrial manufacturing, where machines run at high speeds and temperatures, lubricants play a critical role in reducing friction, minimizing wear and tear, and ensuring the smooth functioning of equipment. Among the myriad additives and compounds used in lubricants, zinc stearate has emerged as a revolutionary component, earning its place as a game-changer in industrial lubrication.
Although often overlooked in mainstream discussions, the chemical properties, versatility and performance-enhancing capabilities of zinc stearate have made it indispensable in a variety of applications – from plastics to paints and most notably industrial lubricants. This blog post by sakha international delves deep into why zinc stearate is so special, how it works in lubrication systems and why industries around the world are increasingly turning to it.
1. Understanding Zinc Stearate: What Is It?
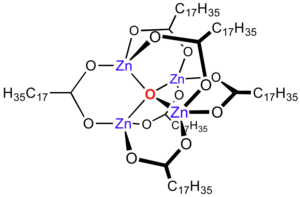
Zinc stearate is a metallic soap that is formed by the reaction of stearic acid—a saturated fatty acid—with zinc oxide. The result is a white, powdery substance that is hydrophobic (repels water), non-toxic, and has excellent lubricating properties. It is often referred to as a “release agent” or “slip agent”, thanks to its ability to reduce friction between surfaces.
Chemically, it is represented as Zn(C₁₇H₃₅COO)₂, and it is insoluble in water but soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial formulations.
2. Key Properties That Make Zinc Stearate Exceptional

Several intrinsic characteristics of zinc stearate make it ideal for use in lubricants:
-
Excellent Lubricity: Zinc stearate provides low friction between metal surfaces, especially in dry lubrication scenarios.
-
Thermal Stability: It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
-
Water Repellency: Its hydrophobic nature prevents water-induced corrosion and oxidation.
-
Non-reactivity: Zinc stearate doesn’t react aggressively with other chemicals, preserving lubricant stability.
-
Versatility: It can be used in both oil-based and solvent-based formulations.
These characteristics allow zinc stearate to function not only as a lubricant but also as a thickener, emulsifier, and anti-caking agent in different industrial applications.
3. Role of Lubricants in Industrial Applications

Before diving into the specifics of zinc stearate’s benefits, it’s important to understand the critical role lubricants play in industry:
-
Reduce Friction and Wear: Lubricants minimize the mechanical resistance between moving parts.
-
Prevent Corrosion: They form a protective layer that shields metal surfaces from oxygen and moisture.
-
Heat Dissipation: Lubricants help in removing excess heat generated by machinery during operation.
-
Contaminant Removal: By carrying away debris, lubricants keep surfaces clean and operational.
Given the demanding nature of industrial environments, any lubricant additive must be robust, stable, and efficient—and zinc stearate meets all these requirements.
4. How Zinc Stearate Enhances Lubricant Performance
Zinc stearate offers multiple functionalities that make it stand out in the formulation of lubricants:
a. Dry Film Lubrication

In applications where traditional liquid lubricants may not be effective or suitable—such as in dusty environments or high-heat conditions—zinc stearate excels as a dry film lubricant. When applied to surfaces, it forms a thin, waxy layer that significantly reduces friction and metal-to-metal contact.
b. Anti-Wear Additive

Zinc stearate acts as an anti-wear agent by forming a protective barrier on metal surfaces. This layer prevents direct contact during machine operation, reducing wear and prolonging the lifespan of machinery components.
c. Thermal Resistance
Its ability to retain its lubricating properties at high temperatures makes it especially valuable in industries such as automotive manufacturing, die casting, and plastics extrusion, where machinery often operates at elevated temperatures.
d. Improved Surface Finish

By reducing friction and facilitating smoother movement, zinc stearate contributes to an improved surface finish in molded and machined components. This is particularly useful in precision manufacturing.
e. Synergistic Effects
When used in conjunction with other additives like molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) or graphite, zinc stearate enhances the overall performance of the lubricant, offering superior load-bearing and anti-seizure properties.
5. Industrial Applications of Zinc Stearate-Based Lubricants

Zinc stearate’s impact is felt across numerous sectors. Some of the most common industries that rely on zinc stearate-enhanced lubricants include:
a. Plastics and Polymer Processing

Zinc stearate serves as an internal and external lubricant during plastic extrusion and injection molding. It reduces melt viscosity, improves mold release, and enhances the surface finish of plastic products.
b. Metalworking

In forging, stamping, and metal forming operations, zinc stearate acts as a die-release agent and dry film lubricant. It minimizes tool wear, improves metal flow, and reduces defects.
c. Automotive Industry

Zinc stearate is used in the manufacturing of gaskets, seals, and brake pads. It provides noise reduction and heat resistance, enhancing the performance of automotive parts under extreme conditions.
d. Rubber Industry

In rubber Industry, zinc stearate functions as a processing aid and mold release agent, preventing rubber compounds from sticking to molds during curing.
e. Powder Metallurgy
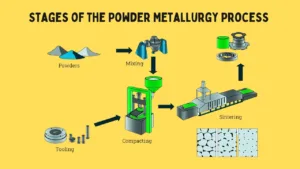
Zinc stearate is added to powdered metals to reduce friction during compaction, aiding in the uniform formation of metal parts with minimal defects.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations

One of the key reasons zinc stearate is gaining popularity is its environmental profile. Compared to some traditional heavy-metal additives, zinc stearate is considered non-toxic and relatively safe. It does not pose major environmental hazards when handled and disposed of properly.
That said, like any industrial chemical, zinc stearate must be used according to standard safety practices. While not harmful through skin contact, prolonged inhalation of fine powders can irritate the respiratory tract, which is why appropriate PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is recommended during handling.
7. Economic and Operational Benefits

For industries operating on thin margins, zinc stearate offers tangible Economic benefits:
-
Cost-Efficiency: It is relatively inexpensive compared to advanced synthetic lubricants.
-
Reduced Downtime: With improved wear resistance and thermal stability, machinery requires less frequent maintenance.
-
Longer Equipment Life: By minimizing friction and corrosion, zinc stearate extends the operational life of industrial machinery.
-
Versatility: A single additive that performs well across different systems reduces the need for multiple specialized products.
8. Innovations and Future Outlook

With ongoing research into advanced lubrication systems, the role of zinc stearate is expected to expand further. Some exciting developments include:
-
Nanotechnology Integration: Researchers are exploring zinc stearate nanoparticles that offer even better dispersion and surface coverage.
-
Hybrid Lubricants: Combining zinc stearate with bio-based or synthetic lubricants to create high-performance green alternatives.
-
Smart Lubrication Systems: Self-lubricating materials that incorporate zinc stearate for intelligent wear response.
Such innovations not only enhance industrial efficiency but also align with global sustainability goals.
9. Case Study: Zinc Stearate in Plastic Injection Molding

To illustrate its impact, consider a manufacturing plant that produces automotive components using plastic injection molding. Before using zinc stearate, the plant faced frequent delays due to parts sticking in molds, which required manual removal and cleaning—reducing overall productivity.
After incorporating a zinc stearate-based mold release lubricant, the following improvements were noted:
-
35% reduction in cycle time
-
50% fewer defective parts
-
20% drop in labor costs for mold cleaning
This real-world example shows how a seemingly small chemical additive can dramatically enhance operational efficiency and profitability.
Conclusion
Zinc stearate has rightfully earned its place as a game-changing additive in the world of industrial lubricants. Its unique blend of lubricating power, thermal and chemical stability, environmental friendliness, and economic value makes it indispensable in modern manufacturing.
From automotive engines to plastic molds, from textile mills to metallurgy labs, the versatile applications of zinc stearate continue to grow. As industries seek smarter, safer, and more efficient ways to maintain and enhance their machinery, the role of innovative additives like zinc stearate will only become more significant.
Whether you’re a formulation chemist, a plant operations manager, or an industrial buyer, understanding the power of zinc stearate could very well be the key to unlocking next-level performance in your lubrication systems.
We are the leading wholesale supplier of best Zinc Stearate
Buy Zinc Stearate in bulk from SAKHA INTERNATIONAL for your business. Contact us at 👉 9810055405.






Leave A Comment