Exploring the Versatility of Refined Glycerine: A Valuable Commercial Asset
Glycerine is a highly versatile and valuable commercial asset that finds applications across various industries. It is widely used across various industries, demonstrating its efficacy in enhancing the quality and performance of different products. First, lets know what is this chemical which is commonly known as Glycerine…
What is Glycerine?
Glycerine – simplest of the alcohols, and also known as Glycerol, is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid with a sweet taste. It is known by its IUPAC name as propane-1,2,3-triol.
Chemically, it is a trihydric alcohol with the molecular formula C3H8O3. Its chemical structure consists of three hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a propane molecule, resulting in its classification as a polyol.
Brief History of Glycerine
- Glycerine was discovered in 1779 by a Swedish chemist named Carl Wilhelm Scheele while experimenting with the hydrolysis of fats. He named it “sweet principle of fat” due to its sweet taste.
- In 1811, French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul coined the term “Glycerine” from the Greek word “Glykys,” meaning sweet, highlighting its sweet taste.
- Over time, advancements in organic chemistry and industrial processes led to the commercial production of Glycerine, initially as a byproduct of soap-making from animal fats or vegetable oils.
- During the 19th and 20th centuries, the understanding of Glycerine expanded, leading to its use in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and more, owing to its versatile properties and applications.
Different Methods of Glycerine Production
Global glycerine production has been influenced by the biodiesel industry’s growth. The volume of glycerine produced annually is in the millions of metric tons.
The production of refined glycerine is spread across regions with significant biodiesel and oleochemical industries. Major producing countries include the United States, Germany, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Argentina.
-
From Fats and Oils:
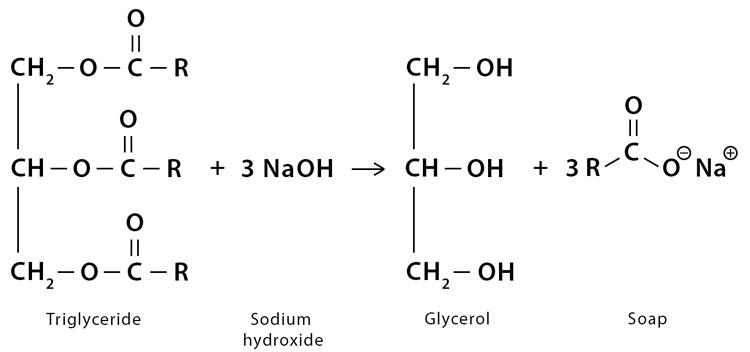
Saponification: Glycerine is a byproduct of the saponification process used to produce soap. During this process, fats or oils react with an alkali (such as sodium hydroxide) to form soap and Glycerin.
Synthetic Production:
Chemical Synthesis: Glycerine can also be synthetically produced from petrochemical sources. This method involves the chemical conversion of propylene or epichlorohydrin into Glycerine.
Processes involved in refining and purifying Glycerine
- Neutralization: Crude glycerine obtained from saponification or synthetic processes undergoes neutralization to remove impurities and excess alkali. This step involves the addition of acids to adjust the pH.
- Distillation: The neutralized glycerine is then subjected to distillation to separate it from water and other impurities. Vacuum distillation is often used to evaporate water and achieve higher glycerin purity.
- Bleaching: To improve color and remove any remaining impurities, bleaching agents like activated carbon or activated earth are used. This step helps achieve a clear, colorless glycerine.
- Deodorization: Glycerine may undergo deodorization to remove any residual odors from the refining process, ensuring it is odorless.
Glycerine, also known as glycerol, possesses a range of properties and characteristics that make it a versatile compound used across various industries. Here’s an explanation of its physical, chemical properties, hygroscopic nature, and its safety features:
Physical Properties of Glycerine
Physical State
Glycerine is a clear, colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid at room temperature (20°C – 25°C or 68°F – 77°F).
Solubility
It is highly soluble in water and miscible with alcohol, acetone, and some oils, contributing to its use as a versatile solvent in various applications.
Viscosity
Glycerine has high viscosity, which means it flows slowly. This property makes it suitable for applications requiring a thick or viscous substance.
Boiling and Freezing Point
Glycerine has a relatively high boiling point of around 290°C (554°F) and freezes at approximately 18°C (64°F), making it useful in certain applications requiring stability at extreme temperatures.
Chemical Properties of Glycerine
Chemical Structure
Glycerine is a trihydric alcohol with a molecular formula C3H8O3. It contains three hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a propane molecule, making it a polyol.

Reactivity
Glycerine is chemically stable under normal conditions, but it can react with certain chemicals under specific circumstances, such as with strong oxidizing agents.
Non-Toxic Nature
Glycerine is considered non-toxic, safe for human consumption, and generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies when used in appropriate concentrations. It’s commonly used in food, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products.
Hygroscopic Nature and Role as a Humectant
Hygroscopicity
Glycerine exhibits hygroscopic properties, meaning it has the ability to attract and hold moisture from the surrounding environment. This characteristic allows it to maintain moisture content in various substances, preventing them from drying out.
Humectant Properties
In skincare products, Glycerine acts as a humectant by drawing moisture from the air and binding it to the skin, helping to keep the skin hydrated, supple, and preventing dryness. It’s a common ingredient in moisturizers, lotions, and other cosmetic formulations.
Non-Toxic and Safe Handling Properties
Safety Profile
Refined Glycerine is generally regarded as safe for handling. It’s non-corrosive, non-irritating, and does not cause skin sensitization in most individuals.
Low Hazard Potential
Due to its low toxicity and safety profile, Refined Glycerine is widely used in various applications, including pharmaceuticals, food products, and personal care items, without posing significant health risks when used appropriately.
Applications of Refined Glycerine
Refined Glycerine plays a crucial role in multiple industries, thanks to its unique multifaceted properties. Its properties as a sweetener, humectant, solvent, and moisturizer make it an invaluable ingredient in various products.
From the food we consume to pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and industrial applications, glycerine’s versatility and unique characteristics make it an essential component in modern manufacturing and everyday products. As industries continue to evolve, glycerine is likely to maintain its significance as a multifunctional compound with wide-ranging applications.Its hygroscopic nature makes it an excellent humectant, capable of attracting and retaining moisture. This makes refined glycerine widely used in the food industry, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and even sustainable energy production.
Refined Glycerine in the Pharmaceutical Industry

a. Solvent and Vehicle:
Glycerine is commonly used as a solvent and a vehicle in the pharmaceutical industry. It helps dissolve and stabilize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in various medications. Glycerine is often present in cough syrups, liquid medications, and topical formulations.
b. Humectant in Formulations:
Similar to its role in the food industry, glycerine acts as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations, helping to retain moisture in creams, ointments, and other topical products.
c. Laxatives:
Glycerine is an active ingredient in certain laxative products. It has a mild laxative effect and is often used to relieve constipation.
Refined Glycerine in the Food and Beverage Industry

a. Sweetener:
One of the primary applications of glycerine in the food industry is as a sweetener. Refined Glycerine is about 60% as sweet as sucrose (table sugar) but has the advantage of being low in calories. It is commonly used in sugar-free and reduced-calorie food products.
b. Humectant:
Glycerine’s hygroscopic nature makes it an excellent humectant, meaning it attracts and retains moisture. In the food industry, it is utilized to maintain the moisture content of various products such as baked goods, confectionery, and processed meats, preventing them from drying out.
c. Thickening Agent:
Glycerine serves as a thickening agent in certain food products. It enhances the texture and viscosity of sauces, dressings, and dairy products.
Refined Glycerine in the Cosmetics and Personal Care Products

a. Moisturizer:
Glycerine is a popular ingredient in skincare products due to its moisturizing properties. It helps to hydrate the skin by attracting and retaining moisture, making it a common component in lotions, creams, and serums.
b. Hair Care Products:
In hair care, glycerine is used to prevent hair dryness and enhance moisture retention. It is found in shampoos, conditioners, and styling products.
c. Soap and Cleansers:
Glycerine is a key component in the production of soaps and cleansers. It contributes to the mildness of these products and helps maintain skin moisture.
Refined Glycerine in the Tobacco Industry
Glycerine’s impact in the tobacco industry is notable for enhancing the smoking experience.
Moisture Enhancement: In the production of smoking tobacco, glycerin is used to add moisture. This not only improves the texture of the tobacco but also influences burn characteristics, providing a smoother and more enjoyable smoking experience for consumers.
Refined Glycerine in the Textile Industry

In the textile industry, glycerine functions as a wetting agent, aiding in dyeing and printing processes. Additionally, it serves as a softening agent, enhancing the flexibility and feel of fabrics.
Refined Glycerine in the Automotive Industry

Refined Glycerine is used in antifreeze formulations in the automotive industry. It prevents the freezing of liquids in the radiator, ensuring optimal engine performance in cold temperatures.
Refined Glycerine in the Paper Industry

Glycerine finds application in the paper industry as a coating or additive. It improves the flexibility and softness of paper products, contributing to the quality of the final materials.
Refined Glycerine in the Plastics and Polymers

As a plasticizer, Refined Glycerine enhances the flexibility and durability of certain plastics and polymers. It influences the material’s properties, making it more malleable and adaptable to various applications.
Glycerine’s versatility underscores its importance, shaping the characteristics of diverse products and ensuring their functionality and consumer appeal.
Benefits of Refined Glycerine
Glycerine, or glycerol, offers several advantages compared to other alternatives in various applications. Here are some key points highlighting the benefits of using glycerin:
Natural and Biodegradable:
Glycerine is often derived from natural sources such as plant oils or animal fats, making it a renewable and biodegradable substance. This contrasts with some synthetic alternatives that may have environmental concerns associated with their production and disposal.
Moisturizing Superiority:
In the cosmetic and personal care industry, refined glycerine’s superior moisturizing properties stand out. Its hygroscopic nature attracts and retains moisture better than some synthetic alternatives, providing effective hydration to the skin and hair.
Humectant Function:
As a humectant, refined glycerine helps retain moisture in various products. In the food industry, it prevents products from drying out and extends their shelf life by maintaining moisture levels. In pharmaceutical formulations, glycerin’s humectant properties contribute to the stability and effectiveness of medications, ensuring they remain in optimal condition.
Sweetening Agent:
Glycerine serves as a low-calorie sweetener in the food and beverage industry. With about 60% of the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar), glycerin provides a sweet taste without the high caloric content. This makes it a preferred option in the formulation of sugar-free and reduced-calorie products.
Solvent and Diluent:
In the pharmaceutical industry, glycerine acts as an effective solvent and diluent. It helps dissolve and stabilize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in various medications. This contributes to the uniform distribution of the drug components and enhances the overall efficacy of pharmaceutical formulations.
Non-Toxic and Safe:
Glycerine is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It has a low toxicity profile, making it a preferred choice over certain chemical alternatives, especially in products meant for personal care and consumption.
Laxative Properties:
Glycerine’s mild laxative properties make it a beneficial component in certain pharmaceutical and healthcare products. It is commonly used in laxatives to relieve constipation by softening stools and promoting bowel movements.
Low Allergenic Potential:
Compared to some synthetic additives, glycerine has a low allergenic potential. It is well-tolerated by most individuals, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including those involving sensitive skin or individuals prone to allergies.
Versatility in Formulations:
Glycerine’s chemical stability and compatibility with a variety of substances make it a versatile ingredient in formulations. It can be seamlessly integrated into various products, including pharmaceuticals, food items, and cosmetics, without compromising stability.
Cost-Effectiveness:
In many cases, glycerine can be a cost-effective option compared to certain synthetic alternatives. Its widespread availability, especially from biodiesel production, contributes to its competitive pricing in the market.
Compatibility in Pharma:
In pharmaceutical formulations, glycerine’s compatibility with a broad range of active ingredients and excipients makes it a preferred choice. It can serve as a solvent, stabilizer, and humectant without negatively affecting the integrity of the medications.
Renewable Source Options:
With the increasing emphasis on sustainability, glycerine sourced from renewable plant-based alternatives, such as soybean oil or palm oil, provides an eco-friendly option compared to certain petrochemical-derived alternatives.
Stability in Antifreeze Applications:
In the automotive industry, glycerine demonstrates stability in antifreeze formulations. It prevents the freezing of liquids in radiators, ensuring the optimal functioning of vehicles in cold temperatures.
Reducing Environmental Impact:
Glycerine’s natural origin and biodegradability contribute to a lower environmental impact compared to some synthetic alternatives. Its use aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly practices in various industries.
Emerging trends in Refined Glycerine Applications and Production Methods
As industries continue to evolve, there are several emerging trends in glycerine applications and production methods. These trends reflect a growing focus on sustainability, technological advancements, and the exploration of new uses for glycerin.
Here are some notable emerging trends:
1. Sustainable Sourcing:
There is a rising demand for glycerine derived from sustainable sources, such as non-GMO (genetically modified organism) crops and waste streams from biodiesel production. This trend aligns with the increasing emphasis on environmentally friendly and socially responsible sourcing practices.
2. Green Glycerine in Cosmetics:
The cosmetics and personal care industry is witnessing a surge in the use of “Green Glycerine” (also called Vegetable Glycerine) sourced from renewable feedstocks. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating glycerin derived from plant-based sources to meet the growing consumer demand for natural and sustainable beauty products.
3. Glycerine as a Green Solvent:
Researchers are exploring glycerin’s potential as a green solvent in various applications. Its biodegradability, low toxicity, and chemical stability make it an attractive alternative to conventional solvents in industries such as cleaning, paints, and coatings.
4. Glycerine in Bio-Based Polymers:
Glycerin is finding applications in the production of bio-based polymers. Researchers are exploring its use as a raw material or co-monomer in the synthesis of sustainable and biodegradable plastics, offering an alternative to traditional petrochemical-derived polymers.
5. Electrochemical Production:
Innovations in glycerine production methods include electrochemical processes. Electrochemical conversion of glycerol offers a potentially more energy-efficient and sustainable way to produce glycerin compared to traditional methods.
6. Glycerine in Agriculture:
Glycerine is being explored for use in agriculture as a bio-based agrochemical. Research suggests its potential as a crop protection agent or as a carrier for delivering biopesticides, showcasing its versatility beyond traditional applications.
7. Glycerine as a Feed Additive:
In the livestock industry, glycerin is being studied as a potential feed additive. Research indicates that it could serve as an energy source for ruminants, offering an alternative to traditional feed ingredients and contributing to the efficiency of animal nutrition.
8. Advanced Refining Techniques:
In glycerin production, there is ongoing research into advanced refining techniques to enhance purity and reduce impurities. Improved refining methods contribute to higher-quality glycerin, meeting the stringent requirements of various industries, especially pharmaceuticals and personal care.
9. Glycerine in Battery Technologies:
Researchers are exploring glycerin-based electrolytes in energy storage systems, including batteries. Glycerin’s electrochemical properties make it a potential candidate for use in sustainable and eco-friendly energy storage applications.
10. Glycerine as a Platform Chemical:
Glycerin is increasingly recognized as a platform chemical with the potential to be transformed into various value-added products. This includes the synthesis of chemicals, fuels, and materials, expanding its role beyond its traditional applications.
11. Integration of Industry 4.0 Technologies:
In refined glycerine production, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, is gaining traction. These technologies enhance process efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and optimize overall production.
As research and development efforts progress, glycerin is likely to continue finding new and innovative uses across a range of industries, contributing to its evolving role in the global market.
Future prospects and potential developments in Refined Glycerine utilization
Here are some websites where you can find reliable information on Glycerin.









Leave A Comment