Zinc stearate might not be a household name, but in the world of paints and coatings, it’s a quiet game-changer. This white, powdery compound plays an essential role in improving product performance and functionality in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Whether you’re a paint manufacturer, a coatings engineer, or simply curious about the chemistry behind surface finishes, understanding zinc stearate’s impact can give you a deeper appreciation for the products that surround us every day.
In this comprehensive article, guided by the expertise of Sakha International, we will explore what zinc stearate is, how it works in paints and coatings, and why it remains a vital additive for improving the performance and quality of finishes.
What is Zinc Stearate?

Zinc stearate is a zinc salt of stearic acid, typically appearing as a fine white powder with a slippery or soapy texture. It is hydrophobic (water-repellent), non-toxic, and insoluble in polar solvents such as water and alcohol. However, it is soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents when heated.
Zinc stearate is classified as a metallic soap, and it’s widely used as a release agent, lubricant, thickener, and emulsifier in various industrial sectors. In the context of paints and coatings, it serves as a multifunctional additive that enhances key product features.
The Role of Zinc Stearate in Paints and Coatings

When formulating paints and coatings, achieving the desired consistency, finish, and durability is crucial. Zinc stearate can dramatically influence these characteristics through several mechanisms.
1. Improved Pigment Dispersion

One of the critical challenges in paint formulation is achieving a uniform and stable pigment dispersion. Poor dispersion can lead to inconsistencies in color, reduced opacity, and poor surface finish.
Zinc stearate acts as a dispersing agent, enabling pigments and fillers to distribute evenly throughout the formulation. It reduces inter-particle attractions, prevents flocculation, and stabilizes pigments in both solvent- and water-based systems.
Benefits:
-
Uniform color distribution
-
Enhanced gloss and opacity
-
Improved storage stability
-
Reduced sedimentation during storage
2. Anti-Settling and Anti-Sagging Properties

Paints, especially those stored for extended periods, are prone to pigment Anti settling. Once settled, these pigments can be difficult to re-disperse.
Zinc stearate increases the thixotropy of the formulation—meaning the paint becomes less viscous under shear stress (like brushing or spraying) and regains viscosity once at rest. This makes the coating easier to apply and prevents sagging or dripping on vertical surfaces.
Benefits:
-
Easier application on vertical and overhead surfaces
-
Prevention of dripping and sagging
-
Consistent film thickness
-
Improved shelf-life
3. Enhanced Slip and Surface Smoothness

Zinc stearate is widely used to improve the tactile and aesthetic qualities of coatings. It imparts a “slip effect”, which reduces the surface friction of the dried film. This makes the coating feel smoother and improves resistance to abrasion and scratching.
Benefits:
-
Smoother finish and improved touch
-
Better resistance to handling and cleaning
-
Reduced wear and tear in high-contact areas
4. Matting Agent
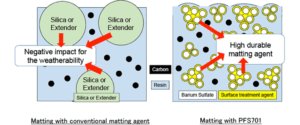
Gloss control is an essential factor in the appeal and function of coatings. High gloss may be desirable in some applications, while a matte finish is preferred in others, such as wall paints or industrial coatings.
Zinc stearate acts as a matting agent, diffusing light reflected from the paint surface and resulting in a softer, more subdued finish.
Benefits:
-
Enhanced aesthetic control
-
Improved visual consistency
-
Ability to tailor finishes from matte to satin
5. Hydrophobicity and Water Resistance
Due to its waxy and non-polar nature, zinc stearate significantly improves the water resistance of paints and coatings. It forms a moisture barrier that repels water and reduces the permeability of the coating layer.
This makes it ideal for exterior coatings or any application requiring resistance to humidity, rain, or water splashes.
Benefits:
-
Better protection against moisture damage
-
Reduced risk of blistering, peeling, and mildew
-
Increased lifespan of the coating
6. Improved Standability

In multi-layer coatings or primer applications, standability is crucial for achieving smooth transitions between layers. Zinc stearate makes coatings easier to sand, reducing effort and improving finish uniformity.
This feature is particularly valued in automotive and furniture coatings, where perfect finishes are non-negotiable.
Benefits:
-
Easier sanding and surface preparation
-
Uniform finish quality
-
Enhanced adhesion of topcoats
7. Compatibility and Versatility

Zinc stearate is compatible with a wide range of resins and solvents, including alkyds, acrylics, polyesters, and epoxies. This makes it a flexible additive suitable for a wide range of coatings such as:
-
Decorative paints
-
Protective industrial coatings
-
Automotive finishes
-
Wood lacquers and sealers
-
Powder coatings
Its versatility allows formulators to tailor products for specific performance needs without compromising compatibility.
Environmental and Regulatory Aspects

With the increasing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly products, it’s important to consider the environmental footprint of additives like zinc stearate.
Safety and Toxicity

Zinc stearate is generally regarded as non-toxic and safe when used in the recommended amounts. It is not classified as a hazardous substance, although inhalation of fine powders should be minimized, as with any particulate material.
Environmental Impact

Zinc stearate is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment. Additionally, it does not contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which aligns well with current efforts to produce low-VOC and eco-friendly coatings.
Challenges and Considerations in Using Zinc Stearate

Despite its many benefits, there are a few considerations formulators must keep in mind when using zinc stearate in paints and coatings.
1. Overuse and Film Defects
Excessive use of zinc stearate can lead to surface issues such as poor inter-coat adhesion or powdery finishes. It’s crucial to maintain optimal loading levels—typically between 0.5% to 3% by weight, depending on the formulation.
2. Dispersion Challenges
Although it aids in pigment dispersion, zinc stearate itself may require pre-dispersion or careful mixing to avoid clumping or “fish-eye” defects in the coating.
3. Compatibility Testing
Despite broad compatibility, it’s advisable to test zinc stearate with specific resins or other additives to avoid unexpected interactions, especially in complex or multi-functional coatings.
Future Trends and Innovations

As paint technology advances, so too does the role of functional additives like zinc stearate. Some future trends and innovations include:
1. Nano-sized Zinc Stearate
Nano-particles offer better surface area and improved dispersion, leading to more effective use at lower dosages. Nano zinc stearate is being explored for high-performance coatings where superior smoothness and water resistance are desired.
2. Sustainable Manufacturing
Green synthesis of zinc stearate using renewable feedstocks or waste materials is being developed, making the additive even more sustainable.
3. Multifunctional Blends
Blends of zinc stearate with other additives (like waxes or silica) are being tailored to offer multi-functional benefits such as anti-blocking, improved slip, and enhanced mechanical strength in a single package.
Conclusion
Zinc stearate might seem like a minor component in the complex world of paints and coatings, but its impact on product performance is significant. From improving pigment dispersion and surface smoothness to enhancing water resistance and sandability, zinc stearate is a versatile additive that addresses multiple challenges in paint formulation.
Its unique set of physical and chemical properties allows manufacturers to produce high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing coatings. When used correctly, zinc stearate not only improves the performance of coatings but also contributes to efficiency in application and long-term durability.
As demand grows for more sustainable, efficient, and high-performing coating systems, zinc stearate will continue to be a valuable tool in the formulator’s arsenal. With advancements in materials science and nanotechnology, its role is only expected to expand further.
For anyone involved in the paints and coatings industry—from formulators and R&D professionals to product managers and quality control experts—understanding the benefits and applications of zinc stearate is essential for staying ahead in a competitive market.
We are the leading wholesale supplier of best Zinc Stearate
Buy Zinc Stearate in bulk from SAKHA INTERNATIONAL for your business. Contact us at 👉 9810055405.






Leave A Comment